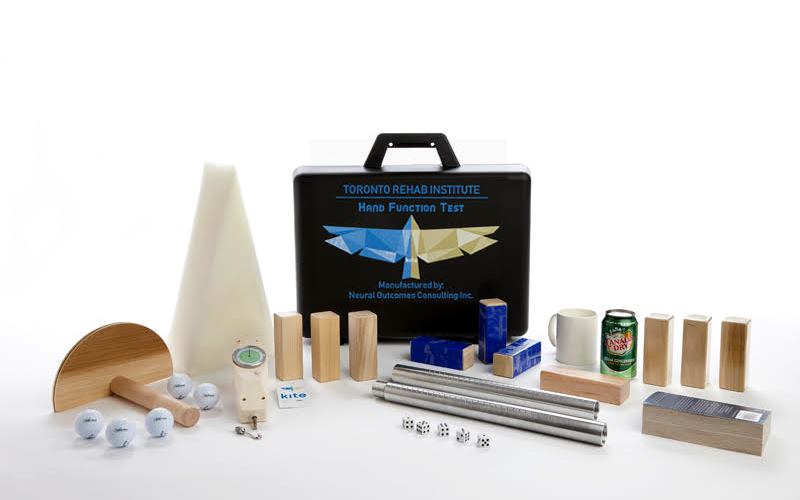
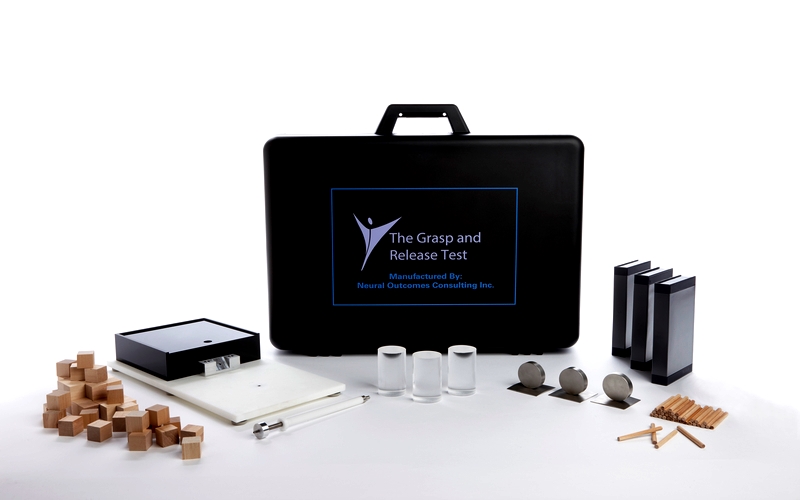
GRASSP and OUTCOME MEASURES
Neural Outcomes Consulting Inc works with health care professionals and researchers to aid the performance of cutting edge research with state-of-the-art trial design. We specialize in oncology, neurological and musculoskeletal disease. With a special interest and experience in the development and use of outcome measures, NOCI optimizes any clinical study or trial with the implementation of the most appropriate outcome measures.
GRASSP Version 1.0
The Graded Redefined Assessment of Sensation, Strength and Prehension (GRASSP) is a multi-domain outcome measure sensitive to the changes in the upper limb throughout disease progression. The GRASSP Research and Design Team, led by Dr. Kalsi-Ryan, has completed it’s development and established its psychometric properties of reliability, validity and responsiveness. GRASSP development and revisions are ongoing. Multi-national collaborations are also defining new analysis approaches for the use of GRASSP in SCI clinical trials. The European launch of GRASSP Version 2 occurred at the 2017 ISCoS Annual Meeting held in Dublin Ireland on October 24-26 while the North American launch took place at the 7th National Spinal Cord Injury Conference that was held on November 9-11, 2017 in Niagara Falls, Ontario. GRASSP Version 2 translated are now available in German, Italian, Czech, Spanish and English.
VERSIONS AND ONGOING DEVELOPMENT
RANGE OF MOTION ASSESSMENT TOOL KITS
The ROM Assessment Kit was developed for Daiichi Sankyo Development LTD (“DSI”): THE ENLIVEN STUDY.
The kit includes a 12 inch, 6 inch and digit goniometers along with a measuring tape. This is a complete kit that enables a clinician to perform any ROM testing. NOCI manufactures and distributes these kits for retail sales.